Difference between revisions of "WFM Assessment"
(Created page with "== Introduction == Traditional WFM on Maturity Curve The WFMLabs.org maturity curve offers a [https://wfmlabs.org/assessment co...") |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 13:06, 23 October 2024
Introduction
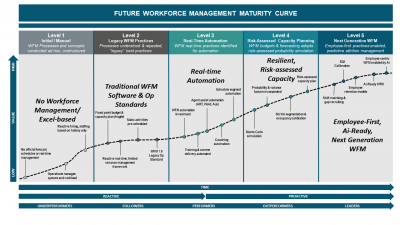
The WFMLabs.org maturity curve offers a comprehensive framework for assessing call centers' operational efficiency and technological advancement. This article examines the distribution of call centers across various maturity levels, emphasizing the prevalence of lower levels (1 and 2) and the scarcity of higher levels (3, 4, and 5) in the current market.
Maturity Levels Overview
- Level 1 - Initial / Manual
- This level characterizes new or under-invested contact centers without official forecasts, schedules, or real-time management. Operations are rudimentary, often relying on reactive hiring and manual workload distribution, leading to compromised customer experience and high business expenses.
- Level 2 - Foundational (Legacy WFM Practices)
- A significant portion of contact centers in 2023 reside here. These centers have invested in people, processes, and traditional WFM software. However, they struggle with "fragile" capacity plans and lack effective methods for managing intraday variance, leading to inefficiencies.
- Level 3 - Progressive
- Centers at this level begin to employ foundational automation components to address intraday variance. They leverage technology beyond core ACD and WFM software for dynamic adjustments, allowing for a more robust forecasting, scheduling, and real-time management approach.
- Level 4 - Advanced
- This level introduces Monte Carlo simulation to build contact center budgets and establish resilient, risk-assessed capacity plans. It acknowledges the natural variance in forecasting and staffing, advocating for probability-based approaches.
- Level 5 - Pioneering
- The highest level, where automation, simulation, and risk-assessed capacity plans are employed to prioritize employee well-being, thereby addressing high turnover rates. These organizations integrate efficiency, customer satisfaction, and employee well-being into their WFM strategy.
Market Distribution
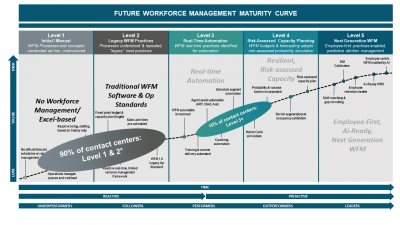
- Majority in Lower Levels: As of 2023-2024, we estimate that less than 10% of call centers are at Level 3 or higher. The majority, approximately 90%, are at Levels 1 and 2.
- Characteristics of Level 1 Centers: Typically, these are smaller call centers with fewer than 200 agents, often relying on spreadsheets instead of WFM software due to cost concerns. These centers are common in small businesses and are not optimized for efficiency.
- Transition to WFM Systems: As call centers grow beyond 200 agents, the need for WFM systems becomes critical. Most larger companies, including Fortune 500 firms, use WFM software packages. However, without automation, these are categorized at Level 2.
- Challenges at Lower Levels: Call centers at Levels 1 and 2 face several challenges, including high attrition rates, inefficient pre-scheduling of off-phone activities, and fragile capacity plans.
Conclusion
This distribution highlights a significant opportunity for growth and advancement in the call center industry. Moving towards higher maturity levels, especially Levels 3 to 5, can lead to more efficient operations, better employee experiences, and improved customer satisfaction. The maturity curve serves as a roadmap for call centers aiming to evolve and leverage the latest in WFM technology and practices.